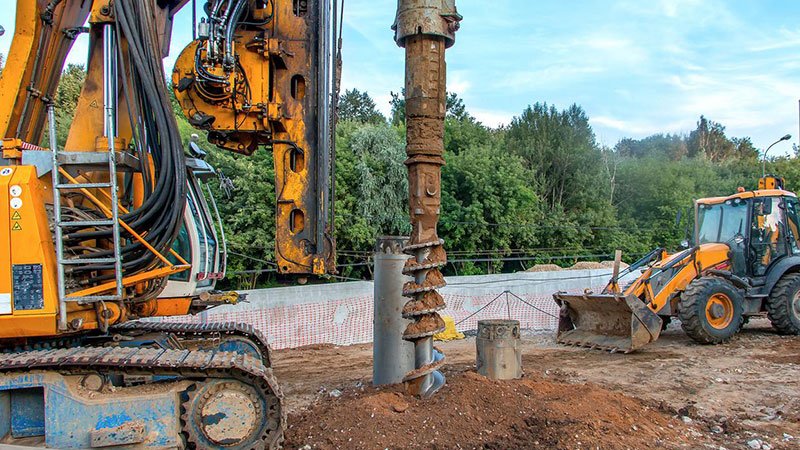
Choosing the wrong drilling method can lead to project delays, excessive costs, and poor results. Rotary drilling has become the industry standard, but understanding its variations is crucial for success.
Rotary drilling is a technique where a drill bit is rotated while applying downward force to create a borehole. The method uses either air or drilling fluid to cool the bit and remove cuttings, making it suitable for various formations from soft soil to hard rock.
In my 15 years of experience with drilling projects worldwide, I've seen how proper understanding of rotary drilling technology can significantly impact project outcomes. Let's explore the key aspects you need to know.
How Does It Work?
Many drilling contractors struggle with efficiency because they don't fully understand the mechanics behind rotary drilling. This knowledge gap often leads to poor performance and equipment damage.
Rotary drilling works through the combination of rotation and downward force (weight on bit). The drill string transfers power from the surface to the bit, while drilling fluid or air removes cuttings and cools the bit. This continuous process creates a clean, stable borehole.
Working with contractors in UAE's demanding conditions, I've found that proper weight-on-bit management and rotation speed control are critical. One client increased their penetration rate by 30% after we helped optimize these parameters.
Key Components
- Drilling rig (power unit)
- Rotary table or top drive
- Drill string
- Drill bits
- Circulation system
- Control systems
Why Choose Rotary Drilling?
The wrong drilling method choice can cost you time and money. Understanding why rotary drilling might be your best option is essential for project planning.
Rotary drilling offers versatility across different formations, superior depth capability, and excellent borehole stability. It's particularly effective for deep wells, hard rock formations, and projects requiring straight, large-diameter holes.
Just last month, I advised a mining company in Africa who switched from cable tool to rotary drilling. Their productivity improved by 200%, despite the initial higher equipment cost.
Main Advantages
- Versatile across formations
- Superior depth capability
- Good borehole stability
- High penetration rates
- Wide range of hole sizes
What is Mud Rotary Drilling?
Mud rotary drilling can seem complex, but understanding its principles helps you maximize its benefits for your project.
Mud rotary drilling uses a drilling fluid (typically bentonite-based) circulated through the drill string to cool the bit and carry cuttings to the surface. The mud also helps stabilize the borehole walls and control formation pressures.
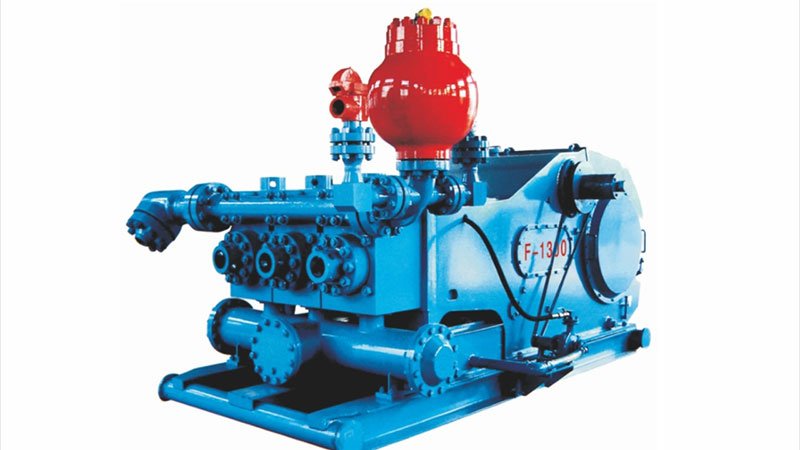

I recently worked with a water well contractor who was struggling with hole collapse issues. After switching to a properly designed mud system, they eliminated the problem and reduced drilling time by 40%.
Mud System Components
- Mud pumps
- Mud pits
- Solids control equipment
- Mud mixing equipment
- Mud testing equipment
What is Air Rotary Drilling?
Air rotary drilling offers unique advantages but requires careful consideration of site conditions and project requirements.
Air rotary drilling uses compressed air instead of drilling mud to cool the bit and remove cuttings. It's particularly effective in hard rock formations and where water conservation is important, offering faster penetration rates and cleaner samples.

During a recent project in Saudi Arabia, switching to air rotary drilling helped our client reduce water consumption by 90% while maintaining excellent drilling performance.
Air System Requirements
- High-capacity air compressors
- Air-water separator
- Dust collection system
- Proper bit selection
- Additional cooling systems
What is Direct Circulation?
Understanding circulation systems is crucial for drilling success. Direct circulation is the most common method but requires proper setup and maintenance.
Direct circulation pumps drilling fluid down through the drill string and up the annulus between the string and borehole wall. This creates a continuous loop that cools the bit and carries cuttings to the surface.
Working with a client in Dubai, we improved their circulation efficiency by 50% by optimizing pump pressure and fluid properties, significantly reducing their drilling time.
System Components
- High-pressure mud pumps
- Surface pipes and hoses
- Drilling fluid tanks
- Treatment systems
- Monitoring equipment
What is Reverse Circulation?
Reverse circulation offers unique advantages for certain applications, but many contractors aren't familiar with its proper implementation.
Reverse circulation moves the drilling fluid and cuttings up through the drill string rather than the annulus. This method is particularly effective for large-diameter holes and when collecting accurate samples is important.
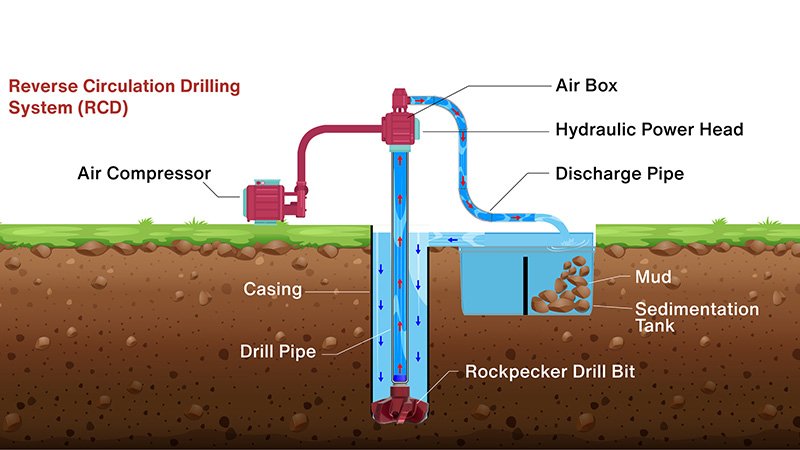
Recently, we helped a mining exploration company switch to reverse circulation for their sampling program. The change resulted in much more accurate ore grade estimates and better project planning.
Applications and Benefits
- Mineral exploration
- Large-diameter wells
- Reduced water consumption
- Better sample quality
- Less formation damage
Conclusion
Rotary drilling technology offers powerful solutions for various drilling challenges, but success depends on choosing the right method and implementing it correctly. Understanding these fundamentals helps ensure your project's success.